Redundancy
Redundancy refers to the number of copies of data that are available at any time; this supports the failure of copies and ensures continuity of services dependent on the redundancy option chosen. Regardless of the option, data is replicated three times in a storage account for the primary region.
LRS
This is storage that iscopied three times within a single physical location in a chosen region. Data is copied synchronously within the location, typically within the same data center. This is the cheapest replication option that can be chosen and is not intended for business-critical workloads that require HA or resiliency. Protection is provided against server rack and drive failures. The following screenshot illustrates replication for LRS:
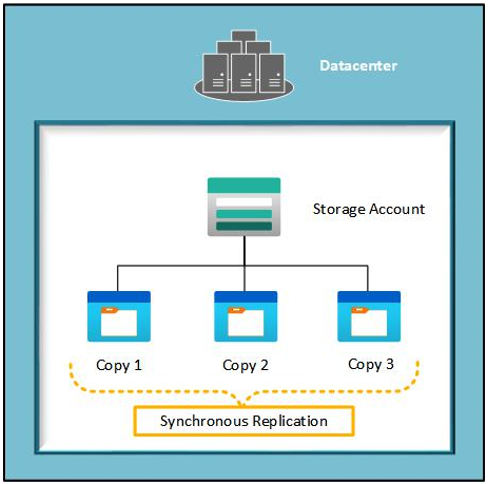
Figure 6.2 – LRS replication
Now that you understand what LRS storage replication is, we will explore ZRS replication.
ZRS
Three copies of data are copied asynchronously across three Azure Availability Zones (AZs) for the selected region; this protects against failure at a data center layer. This redundancy option is recommended for HA within a single region. If a zone becomes unavailable, your data is still accessible both for read and write operations. This option may also be chosen where data residency requirements apply, such as through a compliance standard that the organization aligns to. The following screenshot illustrates replication for ZRS:
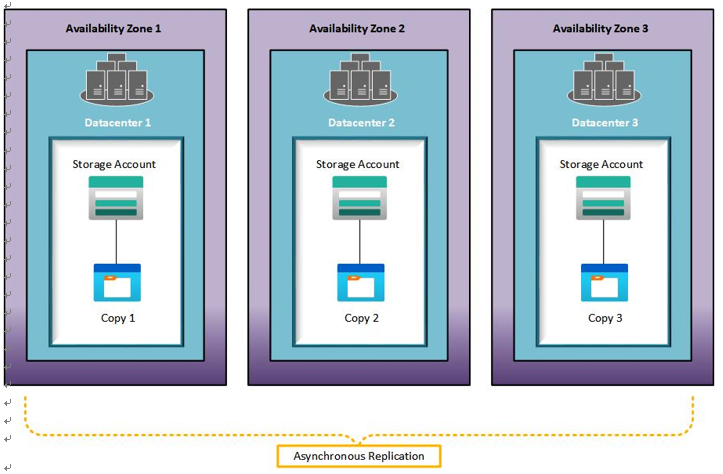
Figure 6.3 – ZRS replication
Now that you understand what ZRS storage replication is, we will explore GRS replication.
GRS
Thisoption is chosen to protect against a region failure while also offering protection within a single data center for each region. Effectively, you get six copies of data (three in each region). Data is copied asynchronously across regions but synchronously within the data center. The following screenshot illustrates replication for GRS:
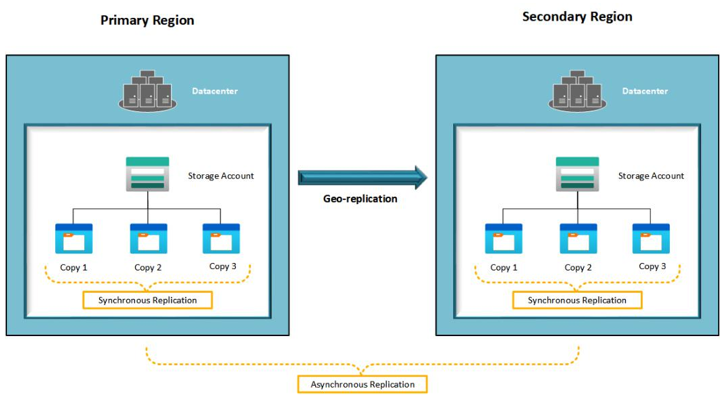
Figure 6.4 – GRS replication
Now that you understand what GRS storage replication is, we will explore GZRS replication.
GZRS
This option is chosen toprotect against a region failure while also offering HA and protection within each region. Effectively, you get six copies of data (three in the primary region distributed across AZs, and three distributed within a data center in the secondary region). Data is copied asynchronously across regions but synchronously within the region and data center. The following screenshot illustrates replication for GZRS/ RA-GZRS:
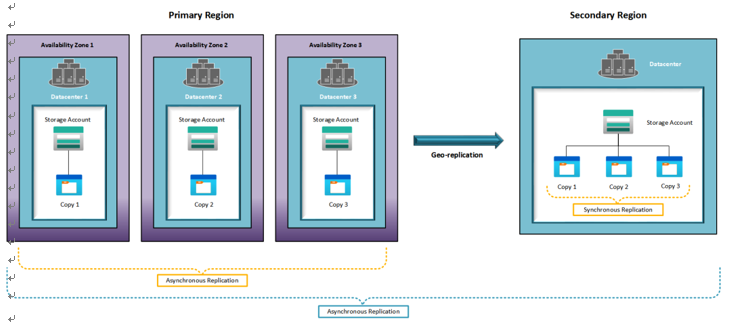
Figure 6.5 – GZRS replication
Now that you understand what GZRS storage replication is, we can conclude this section on storage redundancy types. In the next section, we provide additional reading material to learn more about storage.
Top Tip
The archive tier of storage does not support ZRS, GZRS, and RA-
GZRS redundancy options.

